Deformity Correction Surgeries for Scoliosis and Kyphosis
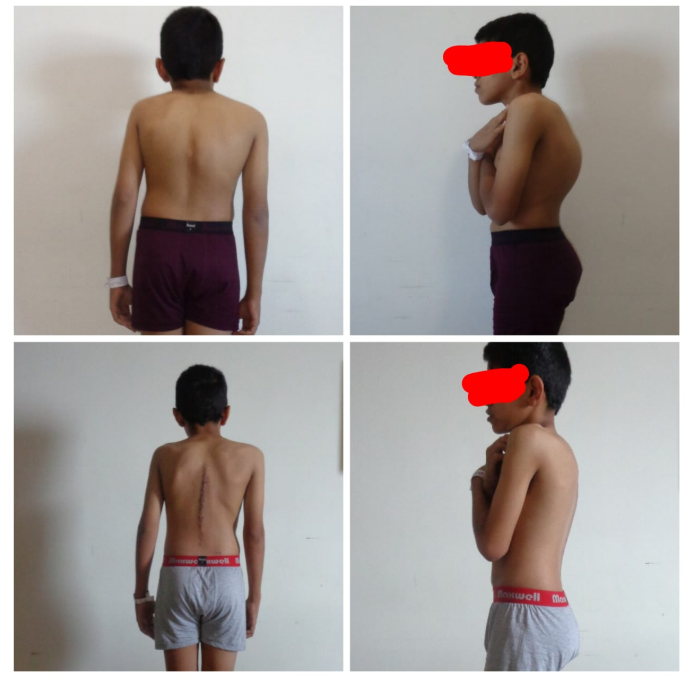
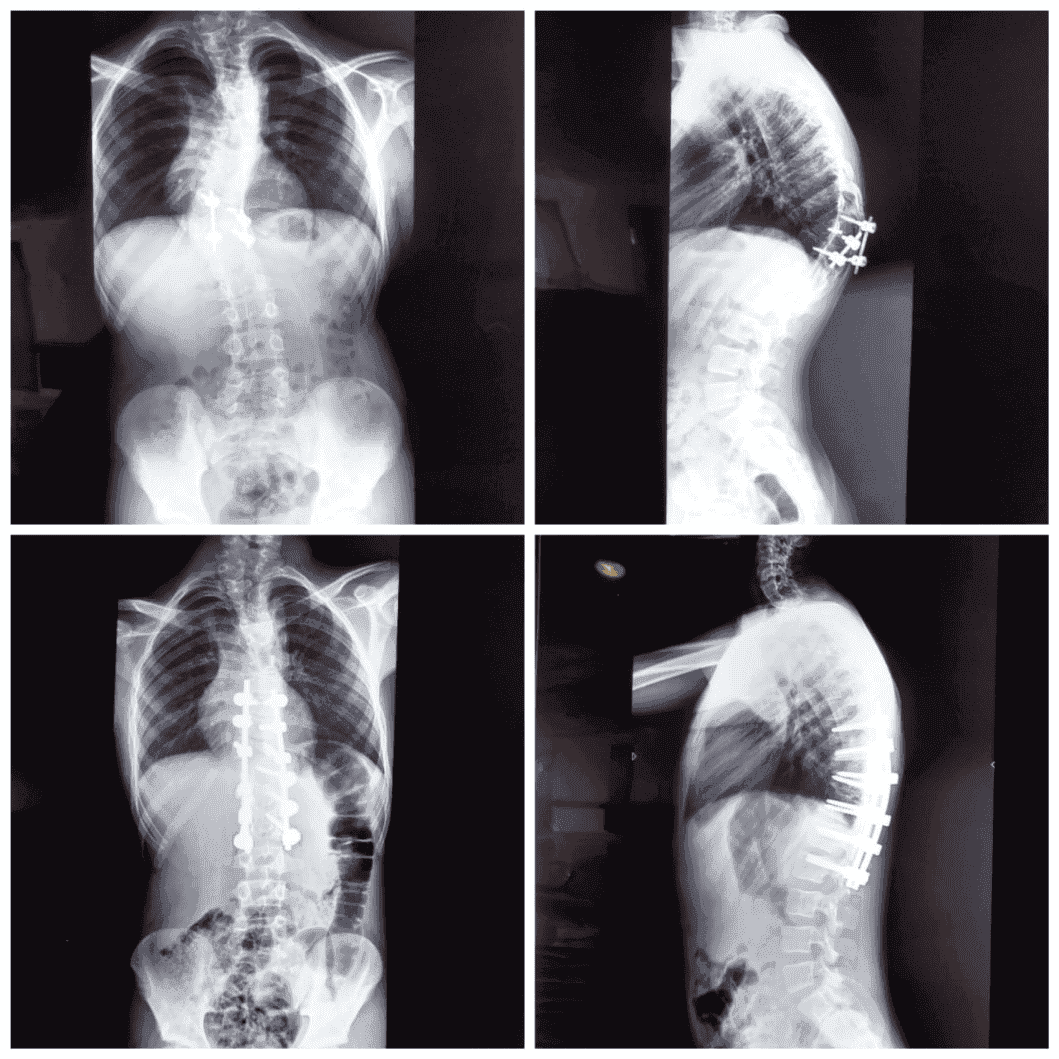
Managed with Assymetrical Pedicle Subtraction osteotomy of D11.
Scoliosis is a sideways curvature of the spine that occurs most often during the growth spurt just before puberty. Most common type of scoliosis is called idiopathic (unknown cause) scoliosis
Most cases of scoliosis are mild, but some spine deformities continue to get more severe as children grow (more commonly between 11-14 years of age). Severe scoliosis can be disabling. An especially severe spinal curve can reduce the amount of space within the chest, making it difficult for the lungs to function properly.
Children who have mild scoliosis are monitored closely, usually with X-rays, to see if the curve is getting worse. In few cases, no treatment is necessary. Some children will need to wear a brace to stop the curve from worsening. Others may need surgery to keep the scoliosis from worsening and to straighten severe cases of scoliosis.
If scoliosis continues to get worse and bracing is either not feasible or not working for the patient, surgery may be considered.
3 Goals of Scoliosis Surgery
Scoliosis surgery typically has the following goals:
- Stop the curve’s progression.When scoliosis requires surgery, it is usually because the deformity is continuing to worsen. Therefore, scoliosis surgery should at the very least prevent the curve from getting any worse.
- Reduce the deformity.Depending on how much flexibility is still in the spine, scoliosis surgery can often de-rotate the abnormal spinal twisting in addition to correcting the lateral curve by about 50% to 70%. These changes can help the person stand up straighter and reduce the rib hump in the back.
- Maintain trunk balance.For any changes made to the spine’s positioning, the surgeon will also take into account overall trunk balance by trying to maintain as much of the spine’s natural front/back (lordosis/kyphosis) curvature while also keeping the hips and legs as even as possible.
The operation for scoliosis is a spinal fusion. The basic idea is to realign and fuse together the curved vertebrae so that they heal into a single, solid bone. This can be achieved safely with tools and technology like neuromonitering and 3D Navigation.
